
Your eye doctor may be able to help you if you're experiencing the symptoms of Chalazion. By taking a complete history about your health, your doctor can diagnose if you have this problem. The doctor will also inspect the eyelashes' texture, oil gland margins, and openings. Most chalazions can be treated with minimal medical attention within a few weeks.
Symptoms
A chalazion, or lump on the eyelid, is called a chalazion. It can grow slowly, but it can expand and cause pain. Although it rarely hurts, it may cause irritated eyes and eyelid inflammation. By looking at the eye and feeling your eyelid, your healthcare provider can diagnose you. If these symptoms continue, you may need to see a doctor. The good news is that chalazion can cause very little harm.
While chalazion can't be contagious it is important that you follow the proper hygiene protocols to lower your risk. After touching your eyes, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly. Also, make sure that your contacts are clean. Also, you should follow your doctor's instructions for wearing contact lenses. Chalazion can also be caused by other conditions such as stye. However, it is not contagious. If you have persistent symptoms, your doctor can prescribe antibacterial medications.
Diagnosis
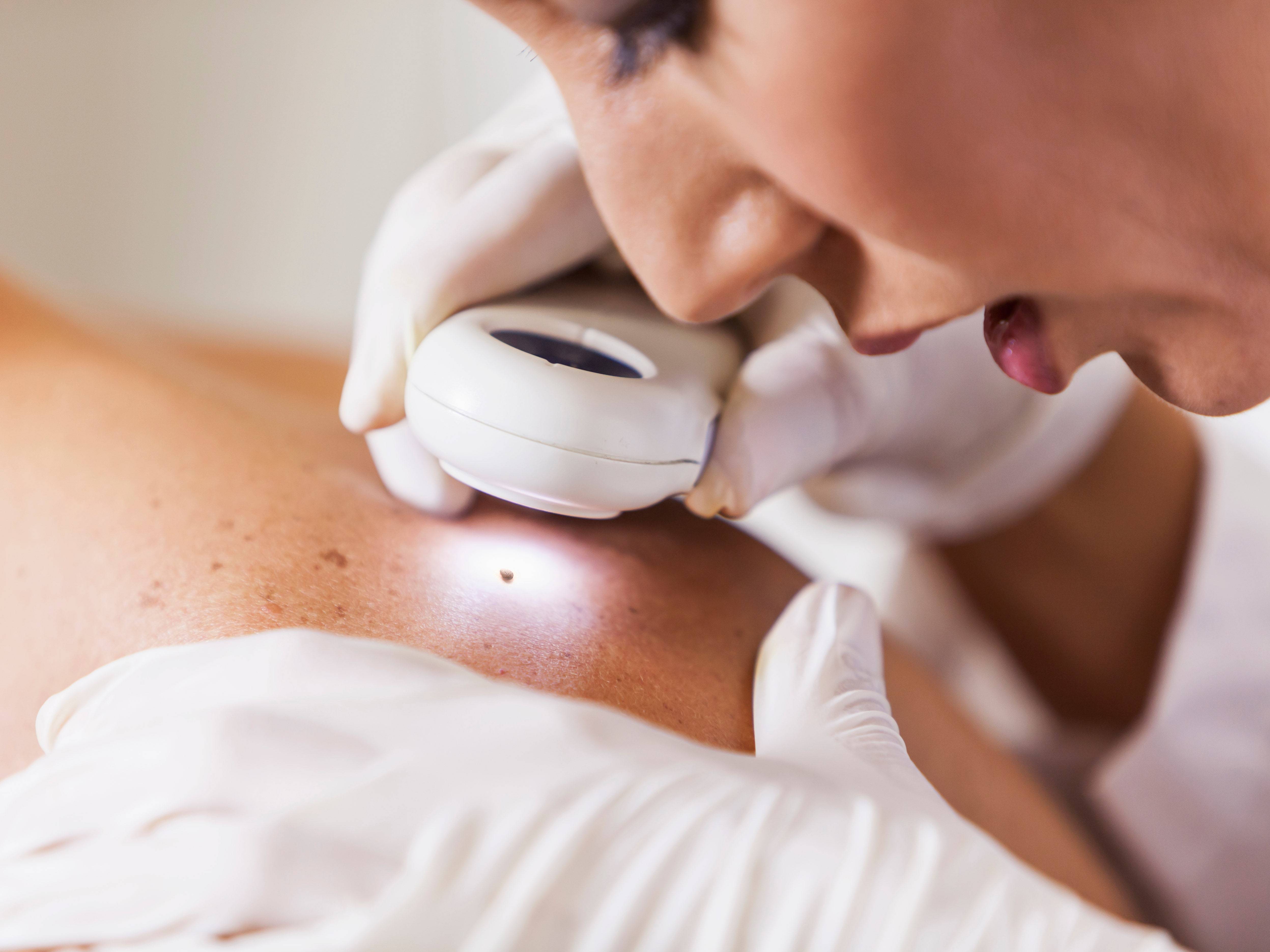
A doctor can diagnose Chalazion by performing a physical exam. The doctor will assess the condition by checking the eyesight and eyelids. He or she may also examine the skin and eyelashes. It could be an indicator of infection or inflammation if the bump becomes large and painful. The eye specialist may also perform a blood test to rule out underlying illnesses. It is possible that the patient has blurred vision. If the condition continues or becomes more severe, a physician may refer the patient directly to an eye doctor.
The most common way to diagnose chalazion involves clinical testing. The diagnosis of chalazion is made by taking detailed notes and performing an examination to determine if it is benign or cancerous. In the majority of cases, no further workup is required. If an alternative diagnosis is needed, a biopsy might be required. A majority of cases are benign and can generally be treated without any further testing. If it recurs it is important to check for malignancy.
Treatment
The severity of the condition will determine the treatment. Some people may feel irritation, pain, and swelling around their eyes. In most cases, chalazion will clear up on its own within a few days. For severe cases, antibiotic eye drops may be prescribed or surgery may be necessary to remove the affected area. Although steroids can be used to lighten the skin permanently, they may also cause it to become more sensitive.
Although chalazion does not spread to other people, you should refrain from touching your eyelids until it has cleared. A specialist in eye care may recommend steroid injections to reduce swelling if it continues. To prevent further complications, it is important that patients wash their hands immediately after removing contacts. Contact lenses should always be cleaned with disinfectant and disposed according to a schedule.
Recurrences
A chalazion is a benign bump on the eyelid. Although often not painful, it can be uncomfortable. Patients should only seek medical attention if their condition worsens. Recurrences, especially in those genetically predisposed, are common. These bumps are common, so what should you do? This condition can be treated by following the steps below.
Most cases can be removed with effective treatment. Although some chalazion recur, most do not. There are many reasons for recurrences. Recurrences can be caused by underlying medical conditions. If you suspect an issue, a biopsy is a good option. You may also be able to rule out more serious conditions. However, it may be a risk factor in recurrent chalazion.